Understand RSSI value to gain more control over your RFID management system
RSSI value is an indicator of signal strength. In practice, it’s used for estimating distance and works a bit like wifi by only reading the tags in a given area.
By applying RSSI filters you can optimize RFID reading and writing conditions for specific applications, so that only tags within a certain distance are registered.
Ultimately, understanding how RSSI value works will give you more control over your RFID management system.
WHAT DOES THE RSSI VALUE TELL US AND WHAT IS IT GOOD FOR?
It’s fairly simple. RSSI stands for “Received Signal Strength Indicator” and it tells us the strength of the signal sent from an RFID tag to an RFID reader.
But what do we use that information for in real-life?
- For measuring the distance between an RFID tag and an RFID reader
- For identifying the movement direction of an RFID tag
- For setting optimal reading and writing conditions
- For analyzing and optimizing the environment
- For locating lost tags
The RSSI value gives us a clue to the distance between an RFID reader and an RFID tag. The environment has a huge effect on the results, but as a rule of thumb, we can say that the higher the RSSI level, the closer the RFID tag is to the reader.
The RSSI value can give us an indication of the distance to the tag, but only after we analyze the environment and take it into consideration.
The RSSI value can also be used to determine the direction that a tag is moving. As the RFID tag moves closer to the RFID reader, the RSSI value increases.
When the RFID tag moves away from the RFID reader, the signal gets weaker. The RSSI value only tells us the distance to the tag, not where it is going.
Several RFID readers are usually required to achieve reliable information about the direction. It is also usually recommended to use supporting techniques, such as “phase difference”, for more reliable results.
Measurements of the RSSI value can be used to analyze the tag reading and writing conditions. The optimal condition is to be able to use as little power as possible for achieving a strong enough signal to perform the RFID actions in question. Different actions require different power outputs and RSSI settings.
Many retail and supply chain operations require a “locate tag” application. The RSSI value can be used for guiding the user closer and closer to the target, much like a Geiger meter.
ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS ON RSSI VALUES
We are constantly surrounded by obstructions and environmental challenges, especially indoors. This can create problems when trying to estimate the location and movements of a tag.
Factors that can cause RSSI levels to vary:
- Metals and other reflecting materials cause the signals to bounce uncontrollably
- Liquid elements that absorb the signal
- Some types of materials that RFID tags are attached to affect the signals
- Blocking objects and constructions between the RFID tag and the RFID reader
- Height difference between the RFID tag and the RFID reader (causes the distance to appear longer)
- Relative orientation of the RFID tag and the RFID reader
APPLYING RSSI FILTERS
During RFID scanning we want the right tags, and only the right tags, to be registered. This can be done by applying a filter that rules out tags with too strong or too weak RSSI values.
In plain English this means that altering the RSSI filter will allow the reader to only see tags that are within the set distance range, e.g. 30-60 cm (12-24 inches), depending on the needs of that particular operation.
When writing tags, it is important that the RSSI value is high, so that the tag has sufficient power. RSSI filtering is used for ensuring that the RFID reader is close enough to the RFID tag to complete the writing operation.
In-store environments and during the supply chain we often run into situations where it is important that a reader only registers tags that are in a certain distance from the reader.
By finding the right filter settings for the particular environment and operation, we can assure that only the right tags are read avoiding unnecessary cross-reading.
RSSI FILTER TEST BY Nordic ID
One of the RF Design Engineers at Nordic ID performed RSSI tests to demonstrate the effects that RSSI filters have on reading distance.
Used settings and equipment:
- Used power level: 100mW
- Tag: UPM RAFLATAC Belt
- Environment: Office environment, room temperature 20±2°C.
- RFID Reader: Nordic ID Sampo S1 UHF RFID Reader
- External antenna (gain: 0dBic)
MIN RSSI setting defines the minimum tag reply power level
MAX RSSI setting defines the maximum tag reply power level
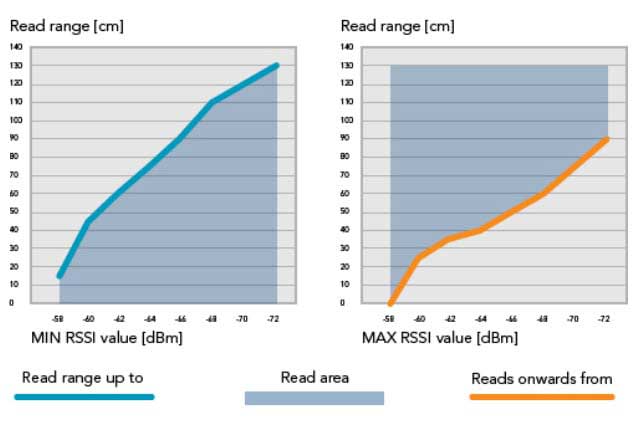
Picture 1. Reading distances with minimum and maximum RSSI value settings.
The blue line demonstrates the effect of using the MIN RSSI setting with a maximum read distance. The orange line describes the minimum read distance by using the MAX RSSI setting.
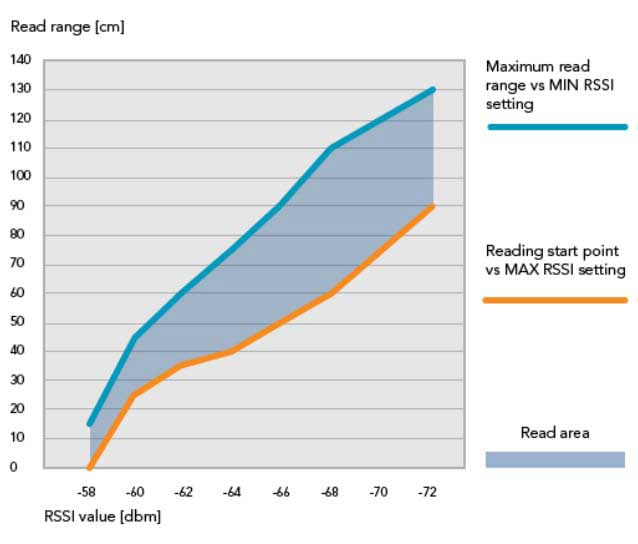
Picture 2. Distance range with same RSSI value
The window that is left open between the two graphs, shown in picture 2, is the area where the tag reply RSSI value is the same for a certain distance range. This means that for example the RSSI level -60dBm can be found between 25-45 cm (10-18 inches) from the RFID reader.
Table 1 indicates the MIN and MAX RSSI values that the reader can get.
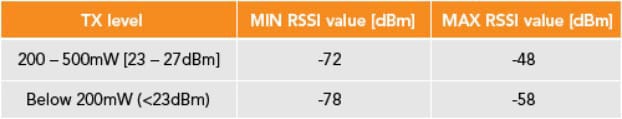
Table 1. MIN and MAX RSSI value.
The test results of this experiment only apply for this specific scenario. If any of the used settings and types of equipment change, the experiment should be redone.
Want to also understand how different power saving options affect your RFID reader’s battery life and power consumption? Read our expert article.